问题:
Given an m x n board of characters and a list of strings words, return all words on the board.
Each word must be constructed from letters of sequentially adjacent cells, where adjacent cells are horizontally or vertically neighboring. The same letter cell may not be used more than once in a word.
Example 1:
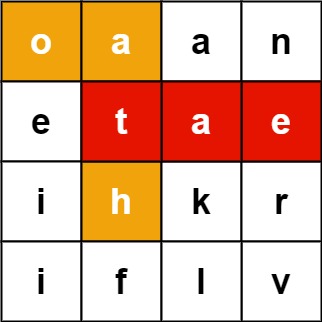 Input:
Input:
board = [["o","a","a","n"],["e","t","a","e"],["i","h","k","r"],["i","f","l","v"]], words = ["oath","pea","eat","rain"]
Output:
["eat","oath"]
Example 2:
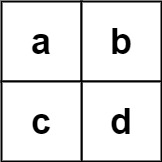
Input:
board = [["a","b"],["c","d"]], words = ["abcb"]
Output:
[]
Constraints:
m == board.lengthn == board[i].length1 <= m, n <= 12board[i][j]is a lowercase English letter.1 <= words.length <= 3 * 1041 <= words[i].length <= 10words[i]consists of lowercase English letters.- All the strings of
wordsare unique.
解答:
深度优先遍历DFS。使用“#”标识了已经遍历的节点的信息,将单词存放到Trie,上下左右四个方向通过调用DFS递归函数在二维数组中进行查找匹配
class TrieNode():
def __init__(self):
self.children = collections.defaultdict(TrieNode)
self.isWord = False
class Trie():
def __init__(self):
self.root = TrieNode()
def insert(self, word):
node = self.root
for w in word:
node = node.children[w]
node.isWord = True
class Solution:
def findWords(self, board: List[List[str]], words: List[str]) -> List[str]:
res = []
trie = Trie()
node = trie.root
for w in words:
trie.insert(w)
for i in range(len(board)):
for j in range(len(board[0])):
self.dfs(board, node, i, j , "", res)
return res
def dfs(self, board, node, i, j, path, res):
if node.isWord:
res.append(path)
node.isWord = False
if i < 0 or i >= len(board) or j<0 or j>=len(board[0]):
return
char = board[i][j]
node = node.children.get(char)
if not node:
return
board[i][j] = "#"
self.dfs(board, node, i+1, j, path+char, res)
self.dfs(board, node, i-1, j, path+char, res)
self.dfs(board, node, i, j-1, path+char, res)
self.dfs(board, node, i, j+1, path+char, res)
board[i][j] = char
参考及引用
图片来自 twitter Ines B @moraimauy